"Data is the oil, some say the gold, of the 21st century—the raw material that our economies, societies and democracies are increasingly being built on.” Joe Kaeser, CEO of Siemens
The new Data Science (DS) profile of the MSE is aimed at the acquisition of in-depth technical and methodological skills in data analysis, artificial intelligence, deep learning, big data, information visualisation and, in general, interoperable, reliable and scalable data-driven services.
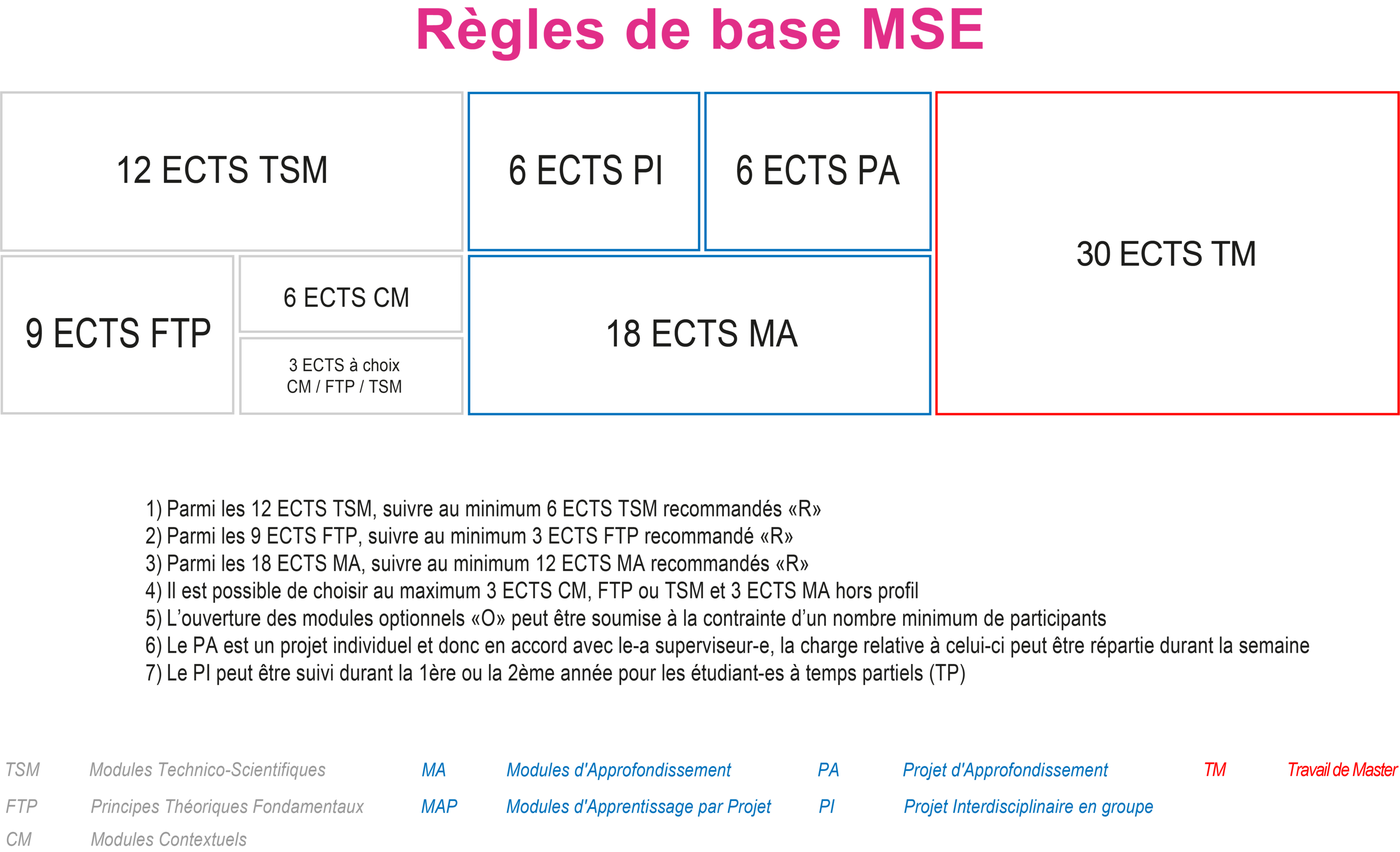
Concept
Why a Master’s in Data Science?
“There is no shortage of enterprise data today. The digital era calls for analytics to be infused in every role, business process, decision and action.” (Gartner)
More than 90% of companies have now identified data science as a key element of their competitiveness. Data science has become a cross-disciplinary skill that is necessary for any engineering company undergoing its digital transformation. Reinforcing this dynamic, new paradigms have emerged in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) that are becoming a reality for companies following on the advances in deep learning, big data and GPU computing. The MSE Data Science profile therefore responds to a current market need for which Master's level courses are required.
What level can students expect to achieve?
Students receiving the Master's degree in Data Science will have developed professional interdisciplinary skills in three key areas of data science. The first is data engineering which covers the techniques of data acquisition, storage and processing. The second is data analytics which covers the processes of converting raw data into actionable information, models and knowledge, by using modern AI techniques among others. The third is oriented towards the production and maintenance of data services that use models from data analytics.
Target group
The Data Science profile is part of the MSE (Master of Science in Engineering), which is a course offered jointly by the Swiss universities of applied sciences. It follows on from the Bachelor's degree. Responding to a current need of engineering companies in all fields, the Data Science profile is open to any student holding a Bachelor of Science in Engineering.
Professional profile
The professional activity targeted by the Data Science profile of the MSE is that of specialist, project manager and/or senior manager in large companies, consulting groups and public administrations that implement projects related to the exploitation of their data, in Switzerland or abroad. The profile prepares you for various professions such as:
- Data Science Engineer
- Data Architect
- Chief Information Officer
- Senior Data Engineer
Skills to be developed
Students receiving the MSE degree in Data Science will have developed professional interdisciplinary skills in the three key areas of data engineering, data analytics and data services. These competencies are described in the Specialisation section below and correspond to identified current needs of the employment market in Switzerland and around the world.
Specialisations
Overview
The Data Science profile is structured around three areas: data engineering, data analytics and data services. These domains are covered by the teaching forms employed in the MSE, including core modules (contextual, fundamental and technical), in-depth modules and projects.
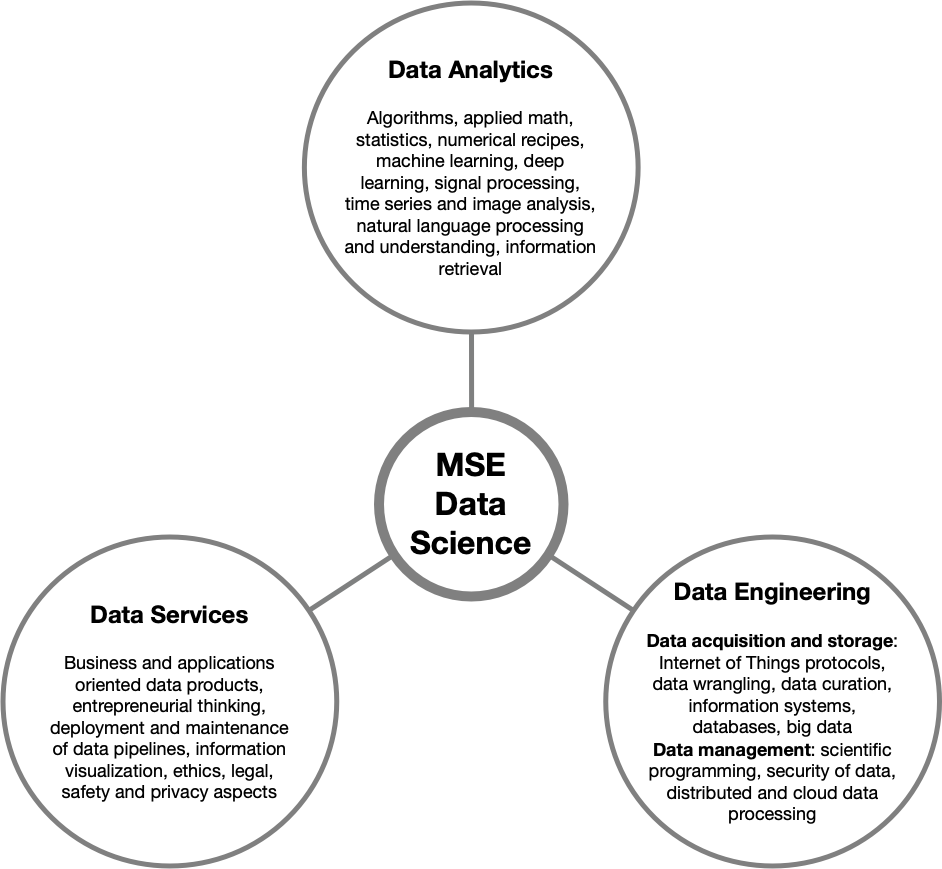
Data Analytics
Data analytics is the process of converting raw data into actionable information, models and knowledge. In this process, models and algorithms are applied to the data. These are constructed using machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, data mining and, in general, applied mathematics. More specifically, the following skills are developed:
- Understand and apply statistical methods to describe and explore data.
- Build models derived from data using data mining, machine learning and deep learning techniques.
- Analyse and plan experiments to build, validate and optimise models according to state-of-the-art practices.
Data Engineering
Data engineering covers data acquisition, storage and processing techniques from an IT perspective. It includes communication protocols with sensors such as those used for the Internet of Things, data flow management and databases including big data solutions. The data processing aspects include techniques of data cleansing, preparation and security. More specifically, the following skills will be aimed at:
- Conceptualize and organise the collection of data from machines and systems used in enterprises, by managing the heterogeneous dimension of data sources including enterprise IoT sensors, structured and unstructured databases, big data technology stacks and online data streams.
- Analyse, plan and organise data storage using technologies appropriate to the needs of the applications, taking into account the constraints of bandwidth, security, volume and variety of data.
- Conceptualise, develop, evaluate and optimise applications capable of efficiently processing data streams, extracting features and applying models.
Data Services
Data services are related to the production of actionable services for businesses. This involves understanding business processes and building the data pipelines that support them, including deployment and maintenance techniques. Other non-technical aspects such as ethics, law, security and privacy are also considerations when deploying these services.
- Build data products by understanding business needs in terms of the data pipeline to transform analytical results into actionable information for businesses.
- Organise the deployment, maintenance and evolution of data services while respecting quality constraints such as Service Level Agreements.
- Understand the non-technical constraints related to the ethical, privacy, security and integrity dimensions of data in companies and public institutions. Organize data services to respect these constraints.
Contact
Jean Hennebert
Head of the DS profile (major)
HES-SO Master
Av. de Provence 6
1007 Lausanne
T + 41 58 900 00 00
mse(at)hes-so.ch